Want polyphenols? Then drink that beer! Or you can get your xanthohumol from Skin Actives.
Polyphenols come in all kinds of shapes and from very different plants. They need antioxidants just as we do.
For some tasty polyphenols have a beer
Let me tell you about hops, a critical ingredient of beer for many centuries. Before hops, beer didn’t taste “right” and did not last very long before going bad.
What is so special about hops?
The “common” hops plant is a very uncommon factory of beneficial phytochemicals, some of them unique to hops. This genus Humulus is related to cannabis, they both belong t the Family Cannabaceae and they have many chemicals in common, like the terpenes myrcene. The hop plants are dioecious, i.e. with unisexual flowers on separate plans that are wind-pollinated. The hops used in the beer industry are the female inflorescences (group of flowers) and are shaped like cones of 2.5 to 5 cm long.
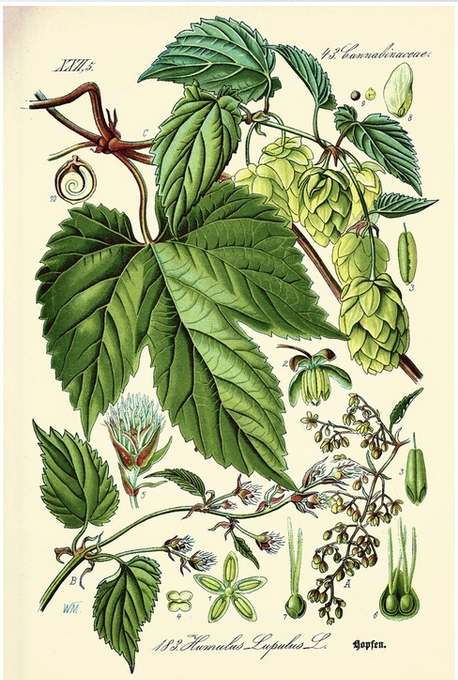
Figure: Humulus lupulus, or common hops.
The hops are used to bitter, flavor and provide a complex fruity and flowery aroma to beer, Hops are also used for various purposes in herbal teas, soft drinks and herbal medicines. They contain polyphenols, mainly phenolic acids, prenylated chalcones, flavonoids, catechins and proanthrocyanidins. Many clinical trials have shown significant reductions in the frequency of hot flushes following the administration of hop-containing preparations.
The (natural) chemicals in hops
The bitterness associated with hops is due to alpha acids, whereas the hops aroma and flavor are due to nonphenolic compounds in the essential oils. There are many beneficial chemicals present in the hops extract but we will concentrate in xanthohumol, the chemical we standardize our extract for.
Xanthohumol
Xanthohumol, a chalcone flavonoid, is one of the chemicals in hops that gives beer its bitterness and flavor. Commercial beers contain less than 0.2 mg of xanthohumol per liter. Here we present a standardized extract from hops, the female inflorescence of Humulus lupulus, that brings the benefits of this natural chemical to your skin.
Xanthohumol benefits:
- Xanthohumol decreased the concentration of reactive oxygen species in vitro, restoring the original concentrations of of enzymatic and nonenzymatic antioxidants after oxidative stress, and lipid peroxidation was attenuated.
- Anti-inflammation, anti-eczema. The transcription factor family NF-κB regulates multiple aspects of innate and adaptive immune functions and serves as a crucial mediator of inflammatory responses. The addition of Xanthohumol decreased the activity of NF-kappa B both in vitro and in vivo after oxidative stress.
- Phytoestrogen, ideal for use in perimenopause and menopause to protect skin and scalp
- Hops are added to beer in part for their preservation power, due to the antibacterial chemicals they contain. Before hops cultivation (earliest recording was 760 AD), beer tended to spoil much faster than it does now.)
- Chemopreventive
Other notable chemicals in hop extract
Bitter acids (alpha-acids/humulone and beta-acids/ lupulone)
While hops alpha acids contain cyclic rings and hydroxyl groups, but the cyclic rings do not have the double bonds required to be classified as a polyphenol. Although many polyphenols are antimicrobial, it is these alpha acids that account for much of hops’ preservative capabilities and one of the reasons why they are added to beer, extending its shelf life. Common alpha acids include humulone and cohumulone.
Hops Polyphenols
Hops polyphenols show significant antioxidant activity, on par with green tea polyphenols. As with many medicinal plants, the amount of polyphenols varies by strain. The amount and type of polyphenols in each strain of hops vary according to the year and location in which the hops were grown and how it is processed after harvest.
8-prenylnaringenin
Phytoestrogenic, cancer preventive. A great natural chemical known to help during peri-menopause and menopause.It is a good ingredient to use for androgenic alopecia. Previous research has shown that hops extract can strongly bind to both estrogen receptors, stimulate alkaline phosphatase activity in Ishikawa cells, and upregulate presenelin-2 and progesterone receptor mRNA in Ishikawa cells.
Kaempferol
Anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant. Kaempferol, a flavonol, has been found to decrease serum interleukin-6 levels, an inflammatory cytokine and suppressed UVB-induced cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) protein expression.
Ferulic acid
A potent antioxidant, ferulic acid protects skin from UV induced erythema by absorbing UV before it reaches the skin (photoprotective) and by preventing lipid peroxidation and the consequent damage to cell membranes. It has also been shown to have chemopreventive activity, preventing a variety of cancers in different tissues including skin. It also has anti-allergic activity. It is used in some ascorbic acid formulations to help prevent its oxidation but there other ways of preventing the oxidation of vitamin C.
Quercetin
Antiviral, senolytic, antitumor. Quercetin is a naturally occurring flavonoid (from the polyphenol group of compounds) found in most plant tissues and it has anti-cancer, anti-ulcer, anti-allergy activity, antiviral, and anti-inflammatory effects that have been attributed to quercetin’s antioxidant activity. Applied topically, was found to protect crucial cell antioxidant systems, including glutathione peroxidase, glutathione reductase, catalase, and superoxide dismutase activities against damage from UVA irradiation. Quercetin will protect skin cells from oxidative stress induced by glutathione depletion, in synergy with ascorbic acid, preventing the carcinogenic effects of some chemical pollutants. It also inhibits membrane lipid of skin cells from peroxidation when exposed to UV light. Another interesting property of quercetin is its anti-elastase activity, i.e. it inhibits the activity of the endogenous enzyme responsible for the breakdown of elastin, a component crucial to skin elasticity. Quercetin also helps with allergy and inflammation; and this is why you will find it in our anti-inflammatory cream which helps with eczema without inducing skin atrophy (the way cortisone products do). Some skin care products contain onion extract as a source of quercetin.
References:
Abdi, F., Mobedi, H., & Roozbeh, N. (2016). Hops for Menopausal Vasomotor Symptoms: Mechanisms of Action. Journal of Menopausal Medicine, 22(2), 62. doi:10.6118/jmm.2016.22.2.62
Chen W, Becker T, Qian F, Ring J. Beer and beer compounds: physiological effects on skin health. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014 Feb;28(2):142-50. doi: 10.1111/jdv.12204.
Gerhäuser C. Broad spectrum anti-infective potential of xanthohumol from hop (Humulus lupulus L.) in comparison with activities of other hop constituents and xanthohumol metabolites. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2005 Sep;49(9):827-31. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.200500091.
Hartkorn A, Hoffmann F, Ajamieh H, Vogel S, Heilmann J, Gerbes AL, Vollmar AM, Zahler S. Antioxidant effects of xanthohumol and functional impact on hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Nat Prod. 2009 Oct;72(10):1741-7. doi: 10.1021/np900230p. PMID: 19757857.
Koo JH, Kim HT, Yoon HY, Kwon KB, Choi IW, Jung SH, Kim HU, Park BH, Park JW. Effect of xanthohumol on melanogenesis in B16 melanoma cells. Exp Mol Med. 2008 Jun 30;40(3):313-9. doi: 10.3858/emm.2008.40.3.313.
Liou SF, Nguyen TTN, Hsu JH, Sulistyowati E, Huang SE, Wu BN, Lin MC, Yeh JL. The Preventive Effects of Xanthohumol on Vascular Calcification Induced by Vitamin D3 Plus Nicotine. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Oct 6;9(10):956. doi: 10.3390/antiox9100956.
Liu M, Hansen PE, Wang G, Qiu L, Dong J, Yin H, Qian Z, Yang M, Miao J. Pharmacological profile of xanthohumol, a prenylated flavonoid from hops (Humulus lupulus). Molecules. 2015 Jan 7;20(1):754-79. doi: 10.3390/molecules20010754.
Lin F-H; Lin J-Y; Gupta R D; Tournas J A; Burch J A; Selim M A; Monteiro-Riviere N A; Grichnik J M; Zielinski J; Pinnell S R (2004) Ferulic Acid Stabilizes a Topical Solution Containing Vitamins C and E and Doubles its Photoprotection for Skin , J Invest Dermatol 125: 826-32.
McCallum, J. L., Nabuurs, M. H., Gallant, S. T., Kirby, C. W., & Mills, A. A. S. (2019). Phytochemical Characterization of Wild Hops (Humulus lupulus ssp. lupuloides) Germplasm Resources From the Maritimes Region of Canada. Frontiers in Plant Science, 10. doi:10.3389/fpls.2019.01438
Sinha P, Srivastava S, Mishra N, Yadav NP. New perspectives on antiacne plant drugs: contribution to modern therapeutics. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:301304. doi: 10.1155/2014/301304.
Stevens JF, Page JE. Xanthohumol and related prenylflavonoids from hops and beer: to your good health! Phytochemistry. 2004 May;65(10):1317-30. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2004.04.025.
Ulusoy, H. G., & Sanlier, N. (2019). A minireview of quercetin: from its metabolism to possible mechanisms of its biological activities. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 1–14. doi:10.1080/10408398.2019.1683810
Yousefzadeh, M. J., Zhu, Y., McGowan, S. J., Angelini, L., Fuhrmann-Stroissnigg, H., Xu, M., Kato, J.I. , Grassi, D. , Wentworth, M. , Burd, C.E., Arriaga E.A. , Ladiges W.L. , Tchkonia, T, James L. Kirkland, J.M. , Robbins, P.D., Niedernhofer, L. J. (2018). Fisetin is a senotherapeutic that extends health and lifespan. EBioMedicine. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.09.015
Zanoli P, Zavatti M. Pharmacognostic and pharmacological profile of Humulus lupulus L. J Ethnopharmacol 2008; 116: 383-96.
DISCLAIMER: These claims have not been evaluated by the FDA and are not intended to diagnose, cure, treat or prevent any disease.
