Chemistry: What is the difference between salicin and salicylic acid?

From: Otto Wilhelm Thomé Flora von Deutschland,
Österreich und der Schweiz 1885, Gera, Germany
More than one thousand years ago, humans in different continents discovered that the leaves and bark of the willow tree could alleviate aches and fevers. With the advent of modern chemistry, in 1828, salicin, the major salicylate in willow bark, was isolated by Johann Buchner. A few decades later, industrial production of synthetic acetylsalicylic acid, trade name Aspirin, was introduced in Germany by Bayer.
In skin care, we use two chemicals of this family: salicin and salicylic acid.
Salicylic acid belongs to a diverse group of plant phenolics, compounds with an aromatic ring bearing a hydroxyl group or a derivative. These ubiquitous chemicals are present in plants for reasons that have nothing to do with human headaches, but are related to the regulation of plant physiology and resistance to pathogens.
It is true that salicylic acid is naturally present in many plants, but plants are not the usual source of the salicylic acid used in skin care. Salicylic acid is present at very low concentrations in plants, where it fulfills the role of a hormone and it would be terribly expensive to extract it from plants. The salicylic acid we use is synthesized in laboratories using organic chemistry methods, not that this matters at all: synthetic and natural salicylic acid are undistinguishable from each other.
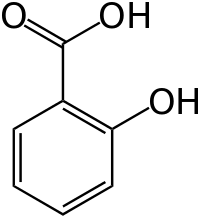
What Properties: antibacterial, keratolytic, anti-inflammatory, etc. Salicylic acid is used in skin care to penetrate the skin in a suitable carrier (alcohol, petrolatum,) where it will exert its anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effect. Salicylic acid works by facilitating the shedding of the cells of the epidermis, opening clogged pores and preventing acne, but at high concentrations it can cause chemical burns like other acids.
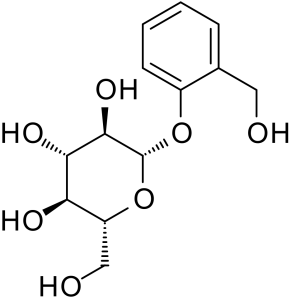
Salicin is an alcoholic β-glucoside. In the human body the molecule is broken and glucose and salicylic alcohol are metabolized separately. By oxidizing the alcohol function the aromatic part finally is metabolized to salicylic acid. The differences in chemical structure make salicin “mild,” non irritating to the skin.
In skin care, salicin and salicylic acid have different applications. The milder, non irritating salicin, is present in our acne and anti-inflammatory products.
Q. Why is salicylic acid called “beta hydroxy?”
A. This weak acid is called beta hydroxy acid in the skin care industry “just because.” No excuse whatsoever.
Q. What is the main difference between salicylic acid and alpha hydroxy acids like lactic acid?
A. They are completely different in their chemical structure, resulting in completely different solubilities.
Q. What is the mechanism of the anti-inflammatory effect of salicylates?
A. Salicylic acid has been shown to suppress the activity of cyclooxygenase (COX), an enzyme that is responsible for the production of pro-inflammatory mediators such as the prostaglandins. It does this by suppression of the expression of the enzyme.
-Dr. Hannah Sivak
