What is melatonin? Why use it on your skin? When?
From my Glossary:
Skin brightener, increases skin elasticity.
Secreted by the pineal gland in response to sunlight, it has been shown that topical application decreases the accumulation of melanin. Topical use of synthetic melatonin appears to be beneficial to the skin in many ways. Used in conjunction with magnesium ascorbyl phosphate (MAP), melatonin improves skin elasticity. It may also help with mouth sores (stomatitis), decrease the side effects of radion therapy on the skin and improve skin texture. Melatonin may help improve hair texture in female alopecia.
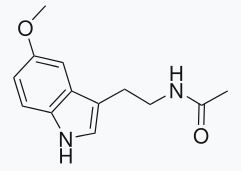
Figure: Melatonin chemical struture
A bit more information: Melatonin (N-acetyl-5-methoxy tryptamine) is synthesized in our bodies from tryptophan, an amino acid, with serotonin as an intermediate step. Melatonin is a human hormone produced at night by the pineal gland (also present in practically all vertebrates), but it is also made by the skin. Melatonin (also present in bacteria, plants, and fungi) and its metabolites have evolutionarily conserved functions, they provide protection against oxidative damage and can restore cellular homeostasis and cell integrity. Melatonin inhibits UV stimulated activation of cell death (apoptosis). Protective activities of melatonin on mitochondria rely on direct scavenging of reactive oxygen species (ROS*) but also include the maintenance of optimal mitochondrial membrane potential and cytosolic pH
Melatonin seems to protect against radiation-induced cellular damage. You will find it in our Post-radiation cream.
Melatonin lightens the skin. You will find it in our Skin Brightening Cream.
Restores cell integrity and homeostasis. You will find it in SAS Skin Soothing Cream with Hemp Extract and UV Repair cream.
You can also buy melatonin as a powder as add it to a cream or lotion.
Slominski, A. T., Zmijewski, M. A., Semak, I., Kim, T.-K., Janjetovic, Z., Slominski, R. M., & Zmijewski, J. W. (2017). Melatonin, mitochondria, and the skin. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 74(21), 3913–3925. doi:10.1007/s00018-017-2617-7
Claims on this page have not been evaluated by the FDA and are not intended to diagnose, cure, treat or prevent any disease.